Proposal of healthcare according to individual attributes

Research overview
Study of ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism for disease prevention and treatment Focusing on a genetic polymorphism unique to East Asians
Currently, our health is governed by the health administration that broadly considers environmental standards, health guidance, medical care services, etc. however, the underlying scientific grounds of these standards and services do not always consider individual attributes such as genetic diversity of constitution and lifestyle of the individual. Aiming for disease prevention and treatment, taking these factors into account would lead to more rational health care practices. In the present study, we have focused on the rs671 polymorphism in the ALDH2 gene.
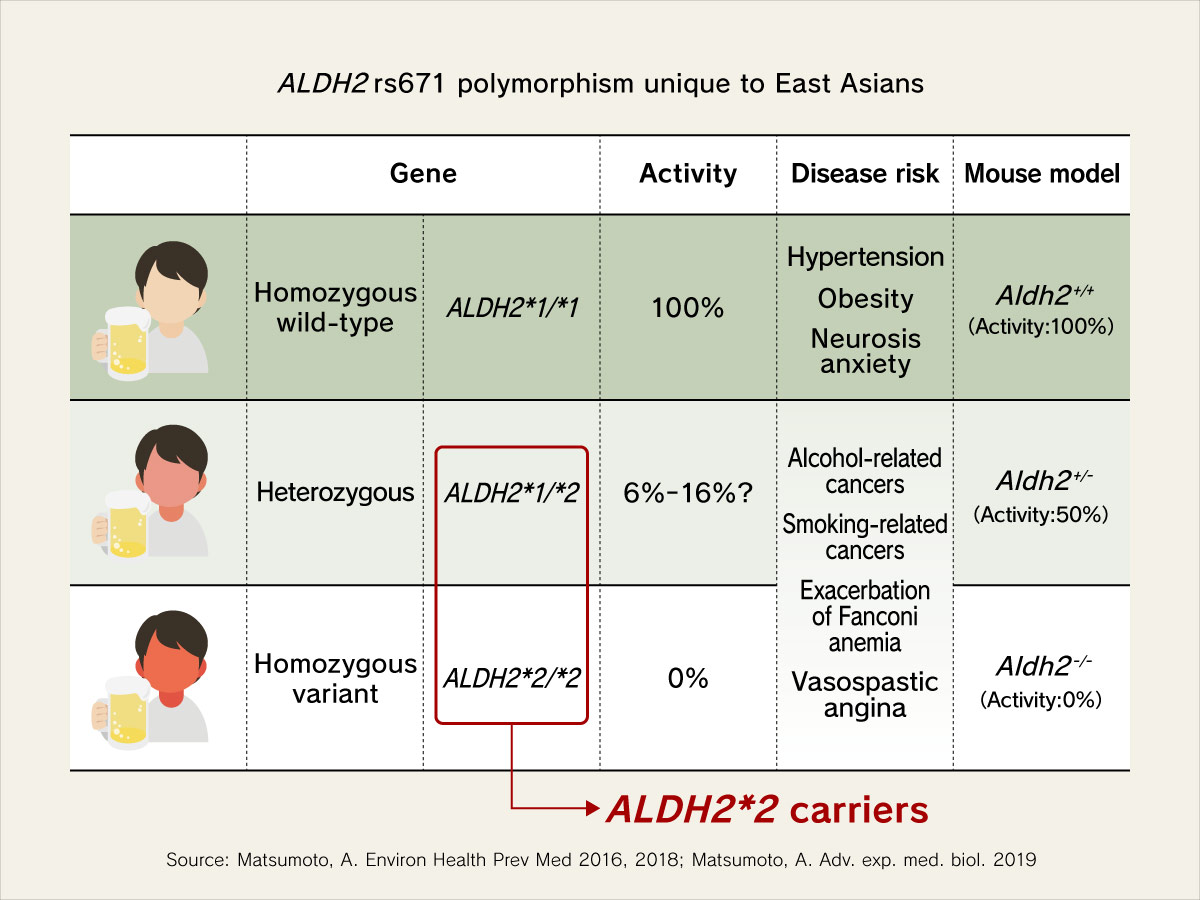
■ ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism
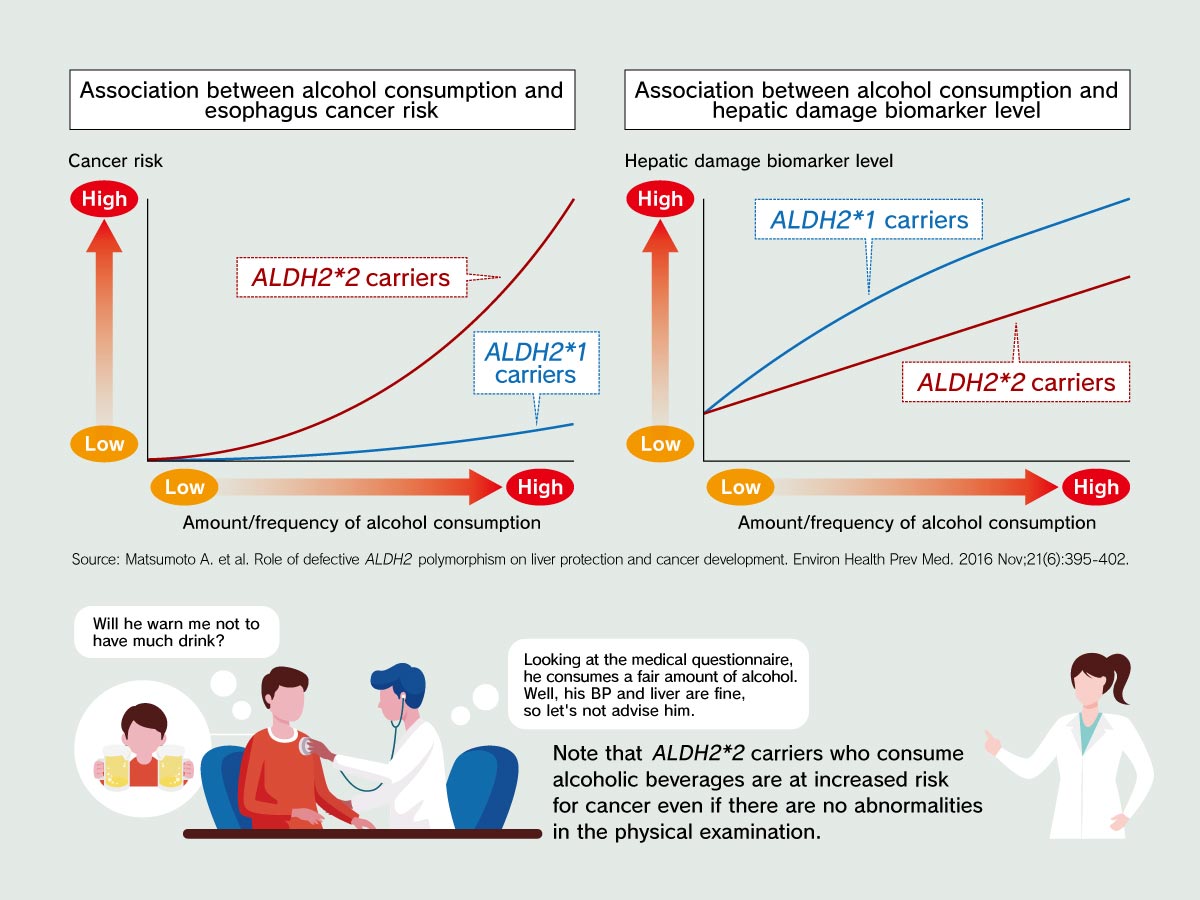
Most people in the world possess the wild type allele of ALDH2 gene (ALDH2*1), while, in contrast, almost half of the Japanese people carry a different allele of this gene, ALDH2*2. The ALDH2*2 variant is known to cause the “Asian flush” phenomena, which is characterized by flushed skin or an increased redness of the skin when alcohol is consumed. Additionally, it is also associated with other characteristics — our previous research has revealed its immunological function; the ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism is linked to the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors; other studies reported that ALDH2*2 carriers, who habitually drink alcoholic beverages, weigh less, have lower blood pressure, and are less likely to show increased blood biomarkers of liver damage, than the wild-type allele who consume alcohol regularly; however, habitual drinking in people with ALDH2*2 is a strong risk for esophageal cancer.
■ Aiming at promoting rs671 awareness
ALDH2*2 carriers tend not to experience significant rise in blood pressure and liver damage indicators upon regular consumption of alcoholic beverages. However, this develops the issue of overlooking excessive drinking in the absence of these biomarkers/ indicators. This may eventually lead to an increase in the occurrence of esophageal cancer. We, hence, are conducting various public relations activities to make people and medical professionals aware of this fact and to avoid the eventual incidence of cancer.
Message
Polymorphisms of ALDH2 rs672 do not have a significant impact on human health alone, but they can significantly alter the hereditary trait; it is closely related to the risk of environmental and lifestyle-related diseases and the effects of medications. However, not enough evidence has been accumulated, perhaps because this polymorphism is uncommon in the world except for East Asia, and naturally, the study of ALDH2 rs672 is highly important in East Asia. In our laboratory, we collaborate with researchers from different backgrounds using various approaches such as in vivo and in vitro experiments, epidemiological studies, and analytical chemistry. Please join us in our laboratory.
Main publications
- Matsumoto A, Nakashima C, Kimura S, Sueoka E, Aragane N. ALDH2 polymorphism rs671 is a predictor of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor efficacy against thoracic malignancies. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):584.
- Matsumoto A, Ito S, Wakamatsu K, Ichiba M, Vasiliou V, Akao C, Song BJ, Fujita M. Ethanol induces skin hyperpigmentation in mice with aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 deficiency. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;302:61-66.
- Matsumoto A. The Bidirectional Effect of Defective ALDH2 Polymorphism and Disease Prevention. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1193:69-87.
- Matsumoto A. The prophylactic importance of polymorphism in aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 gene (ALDH2). Jpn. J. Hyg. 2018;73(1):9-20.
- Matsumoto A, Arcaroli J, Chen Y, Gasparetto M, Neumeister V, Thompson DC, Singh S, Smith C, Messersmith W, Vasiliou V. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1B1: a novel immunohistological marker for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2017;117(10):1537-1543.